In order to meet the growing demand of communication efficiency, we always apply optical circulator in a fiber optic system because the optical circulator minimizes the loss of light. An optical circulator is a device used in optical communications systems, which can be used to separate optical signals that travel in opposite directions in an optical fiber, analogous to the operation of an electronic circulator.
Optical circulator is commonly made of as following optical components: polarizing beam splitter, reflector prism, briefringent blocks, Faraday rotator, and retardation plate.
The operation way of optical circulator is similar to optical isolator. A light travelling in one direction through a Faraday rotator has its polarisation rotated in one particular direction. Light entering the Faraday rotator from the opposite direction has its phase rotated in the opposite direction (relative to the direction of propagation of the light). Another way of looking at this is to say that light is always rotated in the same direction in relation to the rotator regardless of its direction of travel. In a three-port circulator a signal is transmitted from port 1 to port 2, another signal is transmitted from port 2 to port 3, and a third signal can be transmitted from port 3 to port 1. This operation is represented by the following picture.
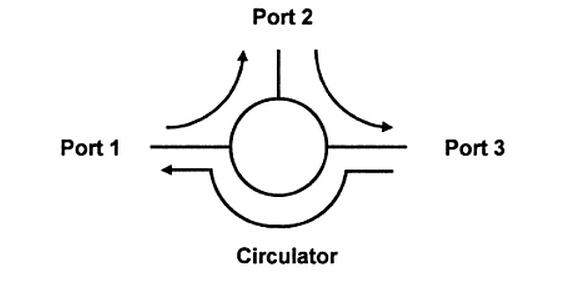
By the number of ports, optical circulators usually falls into three types: 3-port, 4-port and 6-port. In general, 3-port and 4-port circulators are quite common, while the 6-port circulators are less commonly used. No matter which port-type of the optical circulators, optical light is transmitted from any of the port in such circulators can be redirected to any other port.
In terms of operation principles, optical circulators can be divided into three types, traditional, waveguide, and holographic. The traditional optical circulators mainly apply spatial walk-off polarizers (SWPs), Faraday rotators (FRs), and half-wave plates (Hs) to implement its function. The waveguide optical circulators utilize a waveguide Mach–Zehnder interferometer to implement the function of SWPs. The holographic optical circulators apply holographic optical elements to replace traditional SWPs.
According to the polarization characteristics, optical circulators can be divided into two types: Polarization Maintaining (PM) and Polarization Insensitive (PI). PM optical circulator is manufactured with polarization maintaining fiber, making them ideal for polarization maintaining applications such as 40Gbps systems or Raman pump applications. PI optical circulator is a compact and high-performance light wave component. This component is equipped with high isolation, low insertion loss, low polarization-dependent loss (PDL) and high stability and reliability. It is widely used in combination with fiber gratings and other reflective components in dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) systems, high-speed systems and bi-direction communication systems.
Optical circulator is applied in a wide variety of applications within fiber communication system. In advanced optical communication systems, optical circulator is used for bi-directional transmissions, wavelength division multiplexing networks, fiber amplifier systems, optical time domain reflectrometers, etc.
With key features of high isolation, low insertion loss, low cross talk and large bandwidth, optical circulator can be built into the same device as transmitters, receivers, and amplifiers. For more information about optical circulator, please visit Fiberstore.