A network switch has been recognized as one of the most important devices for today’s networking technology. It allows simultaneous transmission of multiple packets and partition a network more efficiently than bridges or routers. The rack mount switch can be installed in a standard 19-inch equipment rack or on a desktop or shelf. So how do you mount a network switch to a rack to establish network wiring connections? Here’s a step-by-step guide to teach you how to mount a network switch to a rack.
Preparations Before Mounting the Network Switch
Before rack mounting the switch, please pay attention to the following factors:
- Location: The site should be at the center of all the devices you want to link and near a power outlet, so that it is accessible for installing, cabling and maintaining the devices in the rack.
- Temperature: Since the temperature within a rack assembly may be higher than the ambient room temperature, check that the rack-environment temperature is within the specified operating temperature range (0 to 40 °C).
- Mechanical Loading: Do not place any equipment on top of a rack-mounted unit.
- Circuit Overloading: Be sure that the supply circuit to the rack assembly is not overloaded.
- Grounding: The switch rack should be properly grounded.
How to Mount a Network Switch to a Rack?
Attach the brackets to the network switch using the screws provided in the mounting accessory.
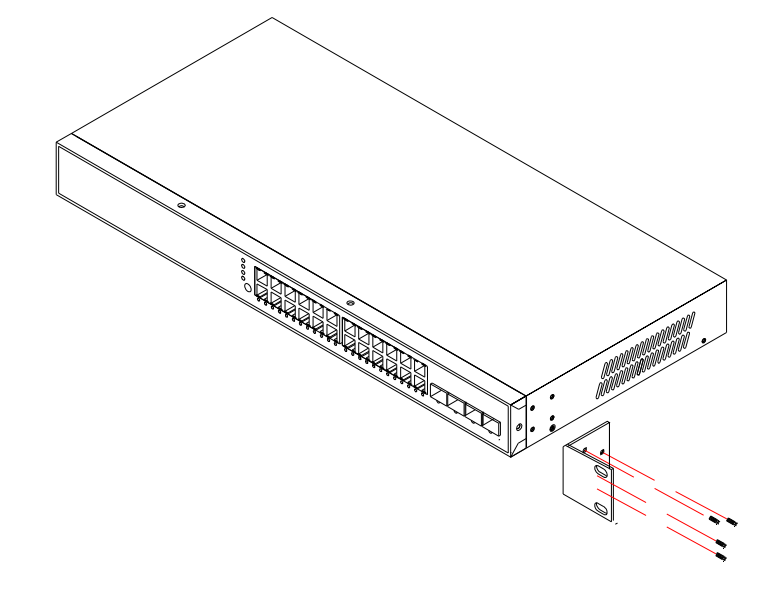
Mount the switch in the rack with the optional rack mount kit, usually using the rack-mounting screws. Be sure to secure the lower rack-mounting screws first to prevent the brackets being bent by the weight of the switch.
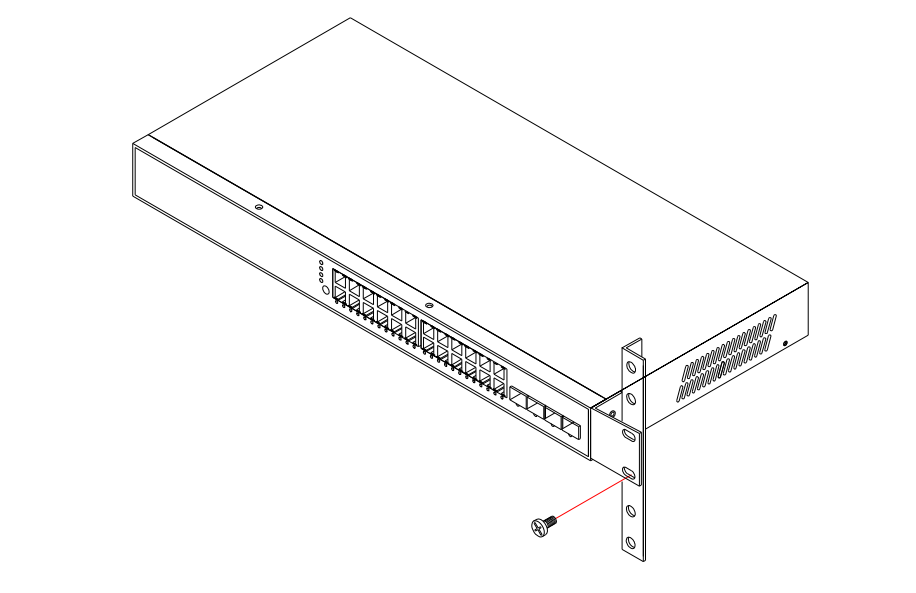
If there is only one data switch to be installed in the rack, then you can make the connection to a power source now. If there are multiple switches to be mounted, you need to install the another switch on the top of the first one in the rack, and then attach the power cords.
After you complete mounting all of the switches in the rack, it’s time to connect the switch rack to the power source. Remember to verify that you have the correct power supply (AC-input or DC-input and the correct wattage) for your configuration.
Caution: To prevent bodily injury when mounting or servicing the switches in a rack, you must take special precautions to ensure that the system remains stable. The following guidelines are provided to ensure your safety:
- This network switch should be mounted at the bottom of the rack if it is the only unit in the rack.
- When mounting the switch in a partially filled rack, load the rack from the bottom to the top with the heaviest component at the bottom of the rack.
- If the rack is provided with stabilizing devices, install the stabilizers before mounting or servicing the switches in the rack.
Establishing Network Wiring Connections
After mounting your network switches to a rack, you can establish the network wiring connections according to your requirements now. If you’re using a Gigabit Ethernet switch, it can be connected to 10, 100 or 1000Mbps network interface cards in PCs and servers, as well as to other switches and hubs. It may also be connected to remote devices using optional SFP transceivers. No matter which type of network switches you are using, make sure that they are securely mounted in the rack and connected to the corresponding networking wiring systems.