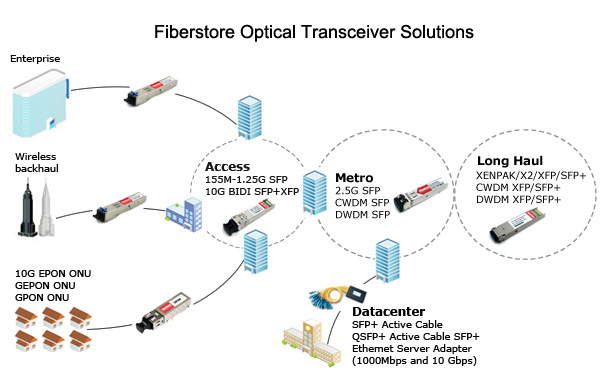
To deploy the optical network, the transceiver module and patch cable are the two basic components. According to the feedbacks of customers from FS.COM, one of the common problems faced by them is what cables they should use for their transceiver modules. To solve this problem, we make this post of patch cable selection guidance. Since the order for 10G transceivers ranks top, we are going to take 10G modules as a reference.
An Overview of 10G Transceiver Module
Transceiver module, also called fiber optic transceiver, is a hot-pluggable device that can both transmit and receive data. By combining a transmitter and receiver into a single module, the device converts electrical signals into optical signals to allow these signals to be efficiently transferred on fiber optic cables. As for the 10G transceiver, it refers to the optical modules with 10G data rate. In FS.COM, there are mainly four types of 10G transceivers: XENPAK, X2, XFP, and SFP+. Even though these optical transceivers are all accessible to the 10G networks, they have different matching patch cables and applications.
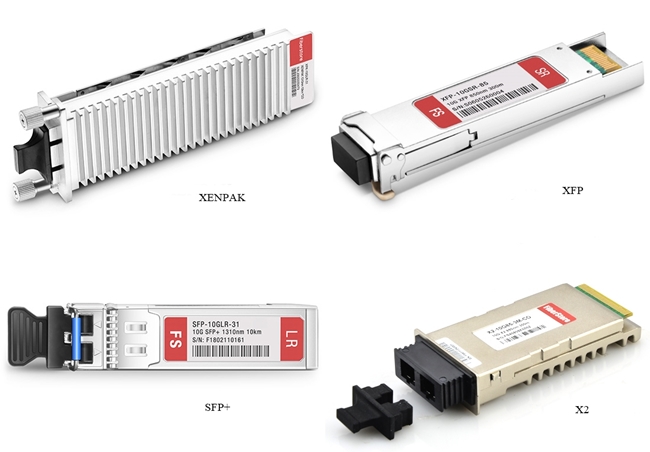
Figure 1: 10G Transceiver Modules
Patch Cable Basics
Apart from optical module, the patch cable is the other vital role in networking. Patch cable, also called patch cord, refers to the copper or optical cable. It’s designed to connect one electronic or optical device to another for signal routing. Conventionally, the patch cable will be terminated with connectors at both ends. For example, the LC fiber cable refers to the optical cable fixed with LC connector. Typically, there are LC, SC, ST, FC and MTP/MPO fiber patch cables. According to different features, we can get various classifications of patch cables, such as fiber types, polishing types, etc.

Figure 2: Patch Cables
Factors to Consider When Choosing Patch Cable for 10G Transceiver Module
Recently, most of the 10G transceiver modules are compatible with different brands and support higher data rates. It will be much easier to choose optical modules for your networking than selecting mating patch cables. Based on most applications, there are three major factors that can be taken into consideration: transmission media, transmission distance, and transceiver module interface.
Classified by transmission media, two types of patch cables can be found in the market: optic fiber cable and copper cable. Correspondingly, there are two kinds of optical transceivers available: copper-based transceivers and fiber optic based transceivers. Copper transceiver modules like 10GBASE-T SFP+, they have an RJ45 interface, connecting with copper cables. Typically, Ethernet cables that support 10G copper-based transceivers are Cat7 and Cat6a cables.
As for the 10G optical modules, they can support higher data rates over optic fiber cables. It will be more complicated to choose fiber cables. Generally, there are multimode fibers and single mode fibers. Based on the specified needs for transmission distance, the answer will be varied.
To select cables, the transmission distance is also an important factor that you need to take care. In the following table, we list the basic information of common 10G transceivers, including their supporting fiber cable types and transmitting distance.
|
Transceiver Type
|
Wavelength
|
Cable Type
|
Transmission Distance
|
|
SR
|
850 nm
|
MMF
|
300 m
|
|
LR
|
1310 nm
|
SMF
|
10 km
|
|
ER
|
1550 nm
|
SMF
|
40 km
|
|
ZR
|
1550 nm
|
SMF
|
80 km
|
As for fiber cables, single mode fiber is used for long-distance transmission and multimode fiber is for short distance. In a 10G network, the transmission distance of single mode fiber (OS2) can reach from 2 km to 100 km. When it comes to multimode fibers, the transmission distances for OM1, OM2, OM3 are 36 m, 86 m and 300 m. OM4 and OM5 can reach up to 550 m.
Another factor you need to consider is the transceiver interface. Usually, transceivers use one port for transmitting and the other port for receiving. They tend to employ duplex SC or LC interface. However, for 10G BiDi transceivers, it only has one port for both transmitting and receiving. Simplex patch cord is applied to connect the 10G BiDi transceiver.
Summary
For your 10G network cabling, transceiver module and patch cable are necessary components. With a wide range of patch cables, selecting the right patch cables will be more complex than 10G transceivers. Generally, three major factors can be considered: transmission media, transmission distance, and transceiver module interface. To apply what you have learned in this post in cabling, you can visit FS.COM for all the transceivers and patch cables at one shop.