Over the last decade, developments in cloud computing and an increased demand for flexible IT solutions have led to new technologies that literally transform the traditional data center. Many businesses have moved from physical on-site data centers to virtualized data center solutions as server virtualization has become a common practice.
What Is Data Center Virtualization and How Does it Work?
Data center virtualization is the transfer of physical data centers into digital data centers using a cloud software platform, so that companies can remotely access information and applications.
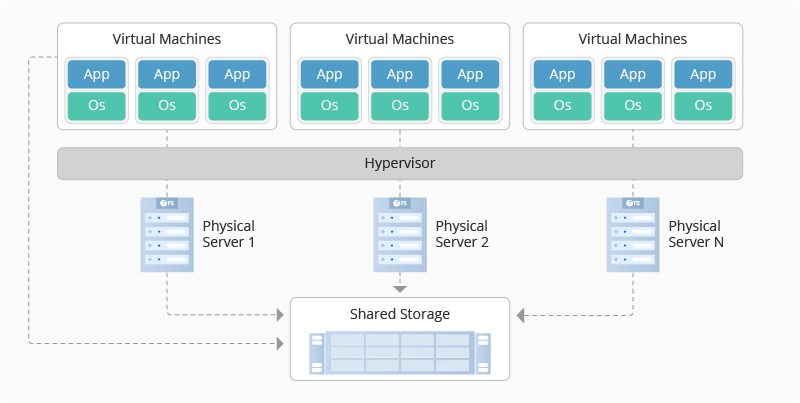
In a virtualized data center, a virtual server, also called a software-defined data center (SDDC) is created from traditional, physical servers. This process abstracts physical hardware by imitating its processors, operating system, and other resources with help from a hypervisor. A hypervisor (or virtual machine monitor, VMM, virtualizer) is a software that creates and manages a virtual machine. It treats resources such as CPU, memory, and storage as a pool that can be easily reallocated between existing virtual machines or to new ones.
Benefits of Data Center Virtualization
Data center virtualization offers a range of strategic and technological benefits to businesses looking for increased profitability or greater scalability. Here we’ll discuss some of these benefits.

Scalability
Compared to physical servers, which require extensive and sometimes expensive sourcing and time management, virtual data centers are relatively simpler, quicker, and more economical to set up. Any company that experiences high levels of growth might want to consider implementing a virtualized data center.
It’s also a good fit for companies experiencing seasonal increases in business activity. During peak times, virtualized memory, processing power, and storage can be added at a lesser cost and in a faster timeframe than purchasing and installing components on a physical machine. Likewise, when demand slows, virtual resources can be scaled down to remove unnecessary expenses. All of these are not possible with metal servers.
Data Mobility
Before virtualization, everything from common tasks and daily interactions to in-depth analytics and data storage happened at the server level, meaning they could only be accessed from one location. With a strong enough Internet connection, virtualized resources can be accessed when and where they are needed. For example, employees can access data, applications, and services from remote locations, greatly improving productivity outside the office.
Moreover, with help of cloud-based applications such as video conferencing, word processing, and other content creation tools, virtualized servers make versatile collaboration possible and create more sharing opportunities.
Cost Savings
Typically outsourced to third-party providers, physical servers are always associated with high management and maintenance. But they will not be a problem in a virtual data center. Unlike their physical counterparts, virtual servers are often offered as pay-as-you-go subscriptions, meaning companies only pay for what they use. By contrast, whether physical servers are used or not, companies still have to shoulder the costs for their management and maintenance. As a plus, the additional functionality that virtualized data centers offer can reduce other business expenses like travel costs.
Cloud vs. Virtualization: How Are They Related?
It’s easy to confuse virtualization with cloud. However, they are quite different but also closely related. To put it simply, virtualization is a technology used to create multiple simulated environments or dedicated resources from a physical hardware system, while cloud is an environment where scalable resources are abstracted and shared across a network.
Clouds are usually created to enable cloud computing, a set of principles and approaches to deliver compute, network, and storage infrastructure resources, platforms, and applications to users on-demand across any network. Cloud computing allows different departments (through private cloud) or companies (through a public cloud) to access a single pool of automatically provisioned resources, while virtualization can make one resource act like many.
In most cases, virtualization and cloud work together to provide different types of services. Virtualized data center platforms can be managed from a central physical location (private cloud) or a remote third-party location (public cloud), or any combination of both (hybrid cloud). On-site virtualized servers are deployed, managed, and protected by private or in-house teams. Alternatively, third-party virtualized servers are operated in remote data centers by a service provider who offers cloud solutions to many different companies.
If you already have a virtual infrastructure, to create a cloud, you can pool virtual resources together, orchestrate them using management and automation software, and create a self-service portal for users.
Article Source: What Is Data Center Virtualization?
Related Articles: