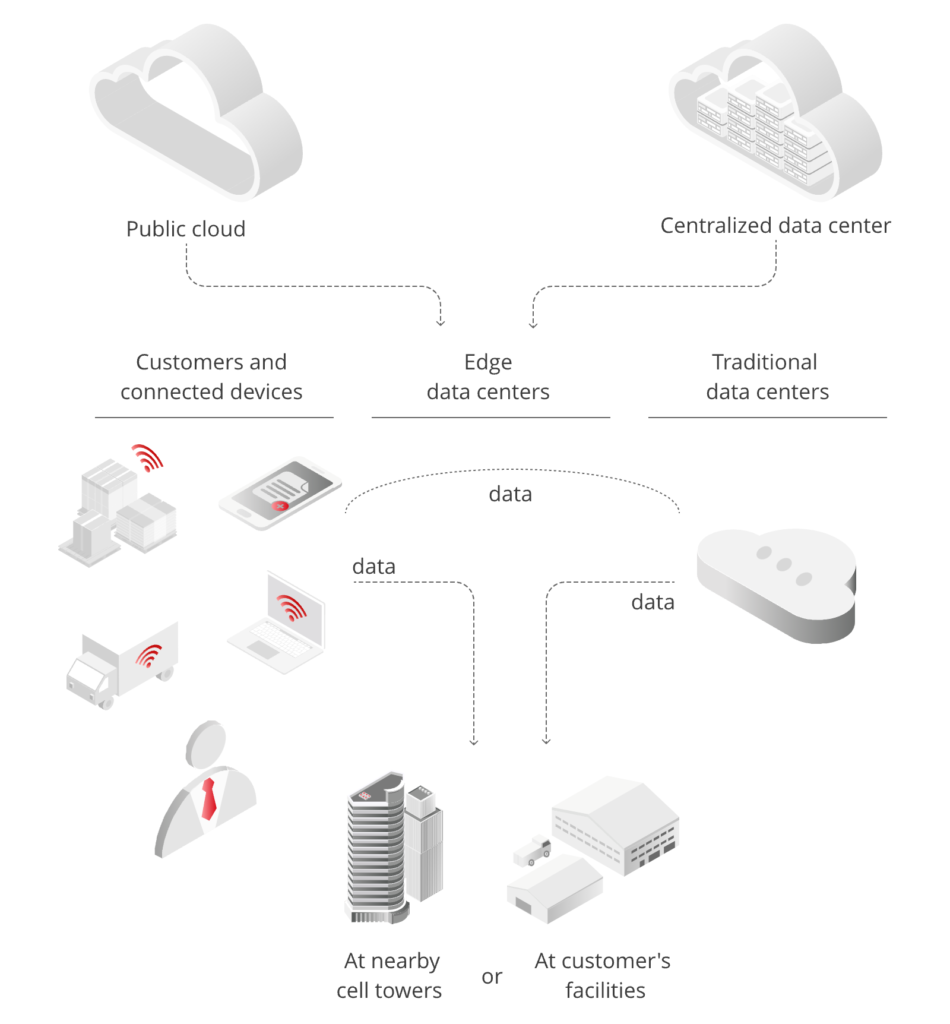
Edge data centers are compact facilities strategically located near user populations. Designed for reduced latency, they deliver cloud computing resources and cached content locally, enhancing user experience. Often connected to larger central data centers, these facilities play a crucial role in decentralized computing, optimizing data flow, and responsiveness.
Key Characteristics of Edge Data Centers
Acknowledging the nascent stage of edge data centers as a trend, professionals recognize flexibility in definitions. Different perspectives from various roles, industries, and priorities contribute to a diversified understanding. However, most edge computers share similar key characteristics, including the following:
Local Presence and Remote Management:
Edge data centers distinguish themselves by their local placement near the areas they serve. This deliberate proximity minimizes latency, ensuring swift responses to local demands.
Simultaneously, these centers are characterized by remote management capabilities, allowing professionals to oversee and administer operations from a central location.
Compact Design:
In terms of physical attributes, edge data centers feature a compact design. While housing the same components as traditional data centers, they are meticulously packed into a much smaller footprint.
This streamlined design is not only spatially efficient but also aligns with the need for agile deployment in diverse environments, ranging from smart cities to industrial settings.
Integration into Larger Networks:
An inherent feature of edge data centers is their role as integral components within a larger network. Rather than operating in isolation, an edge data center is part of a complex network that includes a central enterprise data center.
This interconnectedness ensures seamless collaboration and efficient data flow, acknowledging the role of edge data centers as contributors to a comprehensive data processing ecosystem.
Mission-Critical Functionality:
Edge data centers house mission-critical data, applications, and services for edge-based processing and storage. This mission-critical functionality positions edge data centers at the forefront of scenarios demanding real-time decision-making, such as IoT deployments and autonomous systems.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
Edge computing has found widespread application across various industries, offering solutions to challenges related to latency, bandwidth, and real-time processing. Here are some prominent use cases of edge computing:
- Smart Cities: Edge data centers are crucial in smart city initiatives, processing data from IoT devices, sensors, and surveillance systems locally. This enables real-time monitoring and management of traffic, waste, energy, and other urban services, contributing to more efficient and sustainable city operations.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In industrial settings, edge computing process data from sensors and machines on the factory floor, facilitating real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization of manufacturing processes for increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
- Retail Optimization: Edge data centers are employed in the retail sector for applications like inventory management, cashierless checkout systems, and personalized customer experiences. Processing data locally enhances in-store operations, providing a seamless and responsive shopping experience for customers.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing process data from sensors, cameras, and other sources locally, enabling quick decision-making for navigation, obstacle detection, and overall vehicle safety.
- Healthcare Applications: In healthcare, edge computing are utilized for real-time processing of data from medical devices, wearable technologies, and patient monitoring systems. This enables timely decision-making, supports remote patient monitoring, and enhances the overall efficiency of healthcare services.
Impact on Existing Centralized Data Center Models
The impact of edge data centers on existing data center models is transformative, introducing new paradigms for processing data, reducing latency, and addressing the needs of emerging applications. While centralized data centers continue to play a vital role, the integration of edge data centers creates a more flexible and responsive computing ecosystem. Organizations must adapt their strategies to embrace the benefits of both centralized and edge computing for optimal performance and efficiency.
In conclusion, edge data centers play a pivotal role in shaping the future of data management by providing localized processing capabilities, reducing latency, and supporting a diverse range of applications across industries. As technology continues to advance, the significance of edge data centers is expected to grow, influencing the way organizations approach computing in the digital era.
Related articles: What Is Edge Computing?