CWDM, as an established optical transport technology, is universally employed in optical network for transmission distance extension and fiber exhaust reduction. This technology has evolved for years and now is available for Fiber Channel applications with the rate up to 4.25Gb/s. Moreover, when compared with traditional transmission approach via multiple fibers, embedded CWDM technology also makes economic sense while used in 4G Fiber Channels, and that’s what we are going to address in this article.
The 4G Fiber Channel effectively improves storage area networks (SANs) performance by doubling speed and offering backward compatibility with 2G and 1G systems. With the proliferation of bandwidth-extensive applications, fiber capacity is on the edge of exhaustion. However, the demand for extremely high-capacity data transmissions began to soar. In this case, it is critical for IT technicians to enhance Fiber Channel SAN capacity without increasing costs.
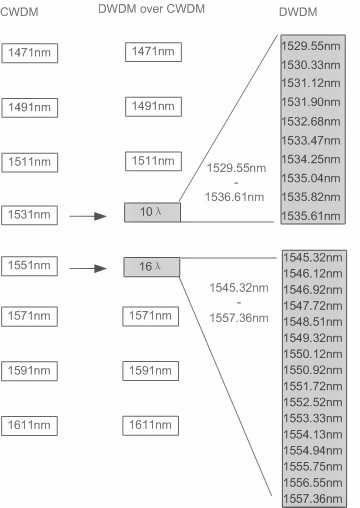
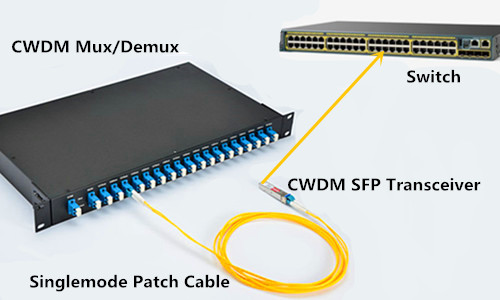
CWDM technology expands fiber capacity by multiplexing optical light signals of different wavelength on a single optical fiber. In a CWDM network, components like CWDM Mux/Demux and CWDM transceivers are indispensable. With CWDM, IP data (Gigabit Ethernet or 10G Ethernet) and storage data (4G/2G/1G Fiber Channel) can be transported over a single fiber infrastructure, eliminating the need for complex protocol conversion.
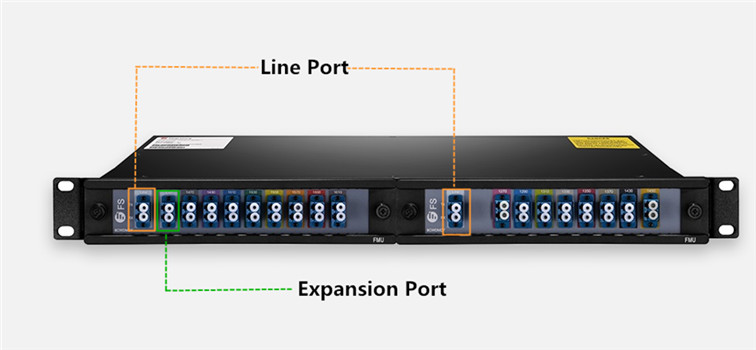
Until now, standalone CWDM solutions are the commonly used methods to transport LAN connections and SAN connections simultaneously between main and recovery sites. Despite that it generates high equipment cost and reduces system reliability. In this case, embedded CWDM emerges as an ideal alternative for use in Fiber Channel applications. Embedded CWDM integrates CWDM optics (like CWDM SFP transceivers) directly into the Fiber Channel switch or Ethernet router, offering better reliability and simplicity. Thus instead of laying more fibers and equipment, users can extend system capacity only by adding new CWDM SFPs, which greatly reduces human labor and overall expenditure.
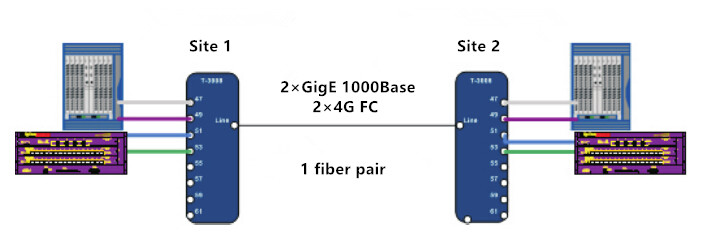
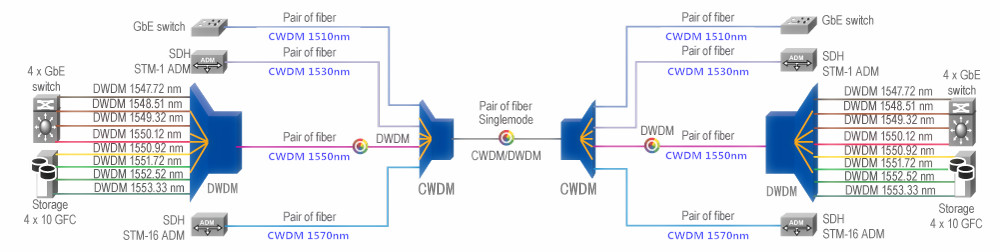
While used for SAN distance extension, CWDM functions to reduce the amount of required WAN fibers. Here we take the example of a SAN extension between a primary site and secondary site. With solution A, the implementation requires several WAN fibers to get the capacity required.
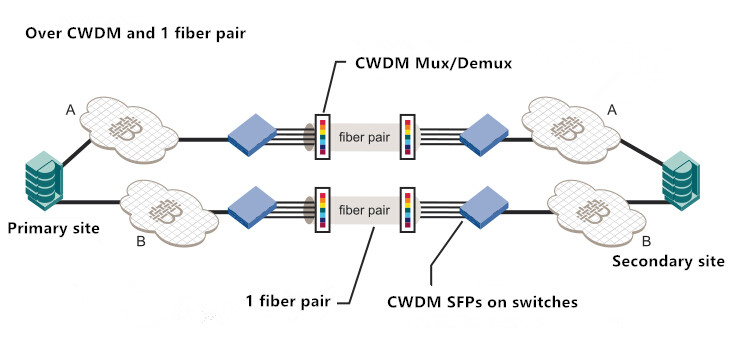
As for solution B, CWDM is adopted to multiplex several signals onto a single fiber pair. CWDM SFPs are directly plugged into the ports from the Fiber Channel switch to generate signals of specific CWDM wavelength. The CWDM Mux combines wavelengths onto a fiber pair, while the CWDM Demux splits these wavelengths into several fiber on the receiver site. Thus the number of required WAN fibers is reduced by the number of wavelengths used.
Embedded CWDM system is easier to operate, which requires no additional network management or training. It introduces more reliability, flexibility and simplicity due to fewer components involved in the system. And its advantages become more evident when it comes to cost: Embedded CWDM solution simply offers lower investment expenditure and operation cost, since it removes the need for adding new fibers and equipment, which can be cost-prohibitive. Even that CWDM SFPs and CWDM Mux/Demux should be involved in CWDM system, the overall cost is just a fraction of multiple fiber transmission.
CWDM solution allows IT managers to achieve network capacity expansion in a more cost-effective, simplified and flexible way. Besides, it also provides enhanced performance and reliability for current need and future growth. For more CWDM solutions and information, visit www.fs.com or contact us via sales@fs.com.