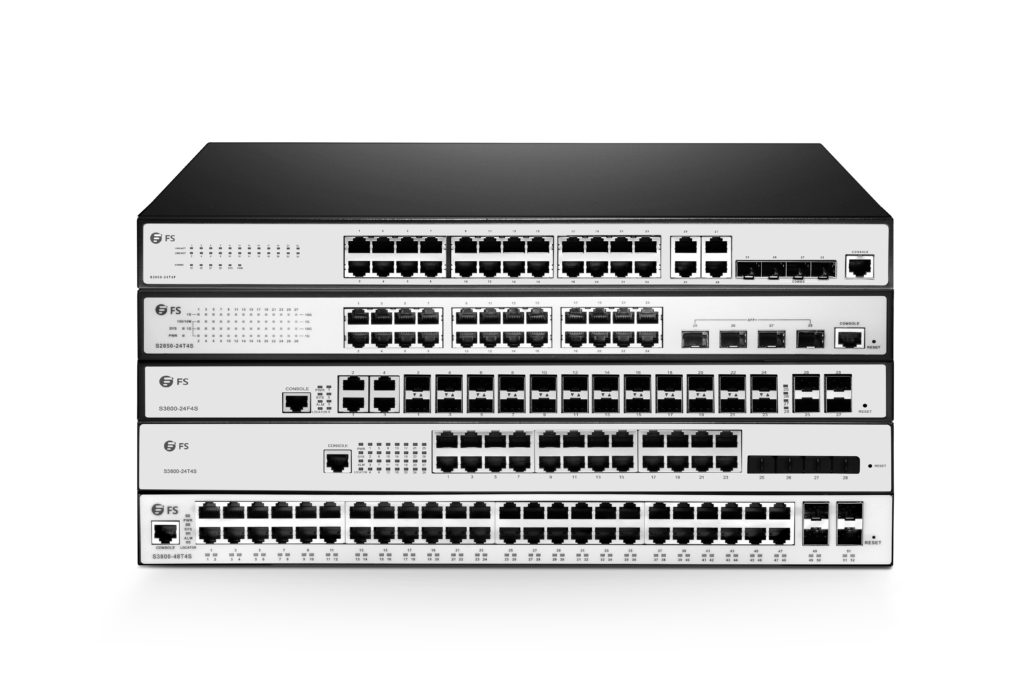
Over the years, the advent of more affordable 10GBASE-T copper solutions has seen growing adoption. And modern business, from sales and marketing to technical support and service, has become increasingly dependent on a fast and reliable network. With a 10GbE RJ45 switch, people can better manage and protect their networks, avoiding network congestion at busy time and shortening the response time to customers and then bring new products to the market faster. Here, we’ll recommend some 10GbE RJ45 switches for your references.
The Reason of Choosing 10GbE RJ45 Switch
10GbE means the speed will be 10 times faster than a normal Gigabit network. Visually, there’s no difference. But if you need to copy large files, a 10GbE switch is necessary. However, why we use the RJ45 type, not the fiber one? Because RJ45 ports can be connected by the copper cables which are something we all are used to. And SFP switch is popular in data centers, which needs to be connected by the expensive fiber cables. RJ45 switch is better since it can be backward compatible with people’s older computers. This is a perfect solution for home use or SMB, since these users would not like to cost too much to buy fibers or new optical equipment. Therefore, a 10GBASE-T switch is their first option.
FS 10GbE RJ45 Switch Recommendations
As a reputable supplier, FS understands the importance of reliable and high performance networks for home users and SMB users. The 10GbE RJ45 switches from FS present the right solution for these users. The following are two RJ45 switches from FS.
|
S5800-48F4S
|
S5850-48T4Q
|
|
|
Description
|
48-port 1Gb SFP and 4-port 10Gb SFP+
|
48 x 10GBase-T ports and 4 x 40Gb uplinks
|
|
Switching Class
|
Layer2/3
|
Layer2/3, data center, Metro
|
|
Switching Capacity
|
176Gbps
|
1.28Tbps
|
|
Forwarding Rate
|
130.95Mpps
|
952.32Mpps
|
|
Latency
|
2.3us
|
612ns
|
S5800-48F4S and S5850-48T4Q switches come with different port designs. With different switching capacity and forwarding rate, they are made to meet various demands.
Both S5800-48F4S and S5850-48T4Q 10GBASE-T switches provide comprehensive L2 or L3 features like MLAG, SNMP etc. in order to meet current and future needs on virtualization, converged networking and mobility. Each port can automatically detect which device is connected to the switch and what speed is needed, then support the device with sufficient speed. Both S5800-48F4S and S5850-48T4Q data switches will give the exact speed like 100MB, 1, 5 or 10 Gigabit that is required without downgrade. In addition, the ports of these switches can be connected with regular Cat5 cables. As a result, there is no need to change into Cat6 or Cat7 wiring. Also, FS data switch uses a Web-based management. Users can easily manage the device through a handy Web-based tool.
Conclusion
10GbE RJ45 switch is the ideal choice for small businesses that want an affordable network switch solution. Whether you are working with a small network of just 10G connections, or a large campus or enterprise network with higher links speed, FS has the right switch for you. Any question about buying issues, please feel free to contact us via sales@fs.com.