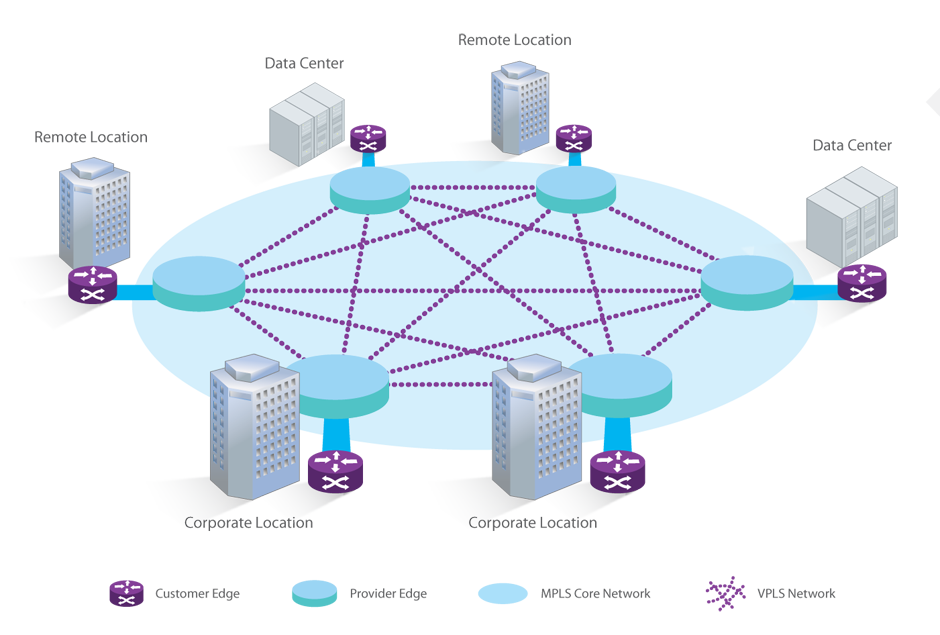
A WAN (Wide Area Network) is a communications network that spans geographically dispersed areas such as across cities, states or countries. A business may have a WAN comprised of cloud services, its headquarters and smaller branch offices, so the WAN is used to connect all sites together. The two most popular WAN connectivity options are MPLS ((Multiprotocol Label Switching) and Ethernet. To help subscribers analyze the differences between MPLS and Ethernet, this side-by-side MPLS vs Ethernet comparison provides a quick overview of the pros and cons of each WAN connectivity option.
What is MPLS?
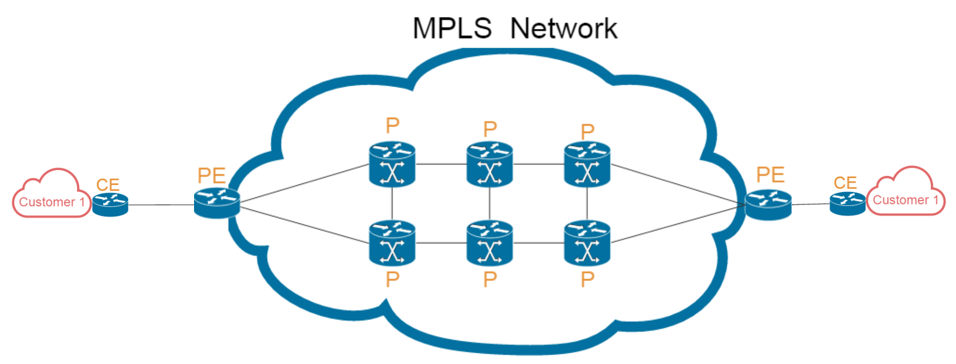
MPLS is a protocol for efficient network traffic flow between multiple locations. MPLS operates similarly on a data switch and router, sitting between layers 2 and layer 3 network. MPLS uses labels for fast packets forwarding and routing within a network. In MPLS network, the MPLS switch (typically Gigabit Ethernet switch and 10GbE switch) transfers data by popping off its label and sending the packet to the next switch label in the sequence. The main benefits of MPLS network service are listed as below.
- Reliability: MPLS is most widely used way to interconnect data centers with remote offices and branches to other branches since MPLS does require an entire block of IPs.
- Service: With MPLS, there is a higher service level agreement that include delivery guarantees for speed and class of service (COS), unlike consumer broadband.
- Labor Cost: MPLS allows businesses to leave WAN routing to the service provider and keep fewer WAN engineers on staff.
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet is a network protocol that controls how data is transmitted over a LAN (Local Area Network), such as those in a room, office, building or campus. As a point-to-point system, an Ethernet network uses Ethernet cables to connect PCs, switches or routers. Most desktop and laptop computers come with integrated an Ethernet card so that it’s easy to connect. Although the functionality of Ethernet is not as high-performing as that of an MPLS network, there are still some merits making it appealing.
- Affordability: Although the scalability of Ethernet is smaller than that of MPLS, Ethernet is more affordable than MPLS, thus becoming the optimal choice for small and medium sized businesses.
- Simplicity: Ethernet is best for connecting one data center to another, including using metro Ethernet to connect corporate sites dispersed geographically.
- Professional Resources: Ethernet gives in-house WAN engineers control and responsibility over routing.
- Disaster Recovery: Ethernet offers low latency and high output, which is ideal for disaster recovery.
- Availability: Ethernet exchanges have made Ethernet WAN services available in more locations.
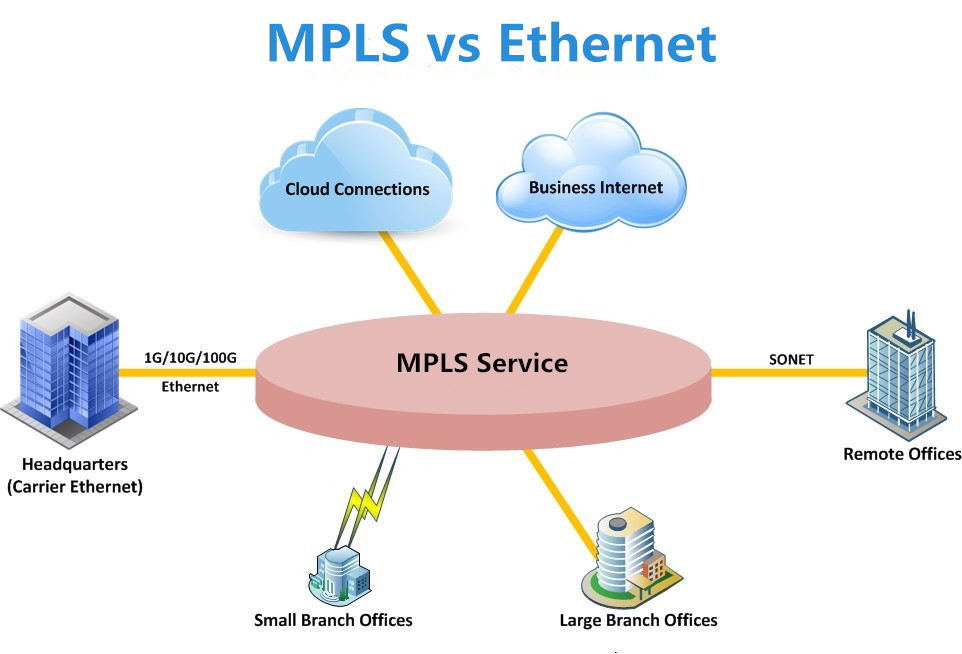
MPLS vs Ethernet for the WAN
Take a closer look at the subtle difference between MPLS vs Ethernet for the WAN connectivity from the chart below.
| Parameter | MPLS | Ethernet |
| Scalability | Scale to over thousands of sites | Scale to up to hundreds of sites |
| Application | Interconnect data centers with branch offices and branches to other branches | Interconnect data centers |
| WAN routing | Leave WAN routing to the service provider and keep fewer WAN engineers on staff | Give WAN engineers control and responsibility over routing |
| WAN protocol behavior | Handle any-to-any connectivity, including voice and video | Offer low-latency and high-throughput, which is ideal for disaster recovery. |
| Quality of service (QoS) | QoS options to enable preferential treatment of latency-sensitive traffic like VoIP | Network engineers can bypass QoS complexity by hooking switches directly to Ethernet pipes |
| WAN management | Complex | Simple |
| Cost | High | Low |
Summary
When weighing the pros and cons of MPLS vs Ethernet, make sure to examine your business needs and understand the resources available within the network, as well as what options exist in your geographic area. Most ISPs nowadays also offer an ISP-managed MPLS service, so they can manage the equipment, and basically get an Ethernet handoff to a switch, which is the so called “MPLS over Ethernet”. No matter which solution you would prefer, your network selection will influence the quality, reliability, service and cost of your WAN connectivity.