The Internet has undergone tremendous changes and broken the barriers from the impossibilities to the possibilities. To seamlessly and securely get access to the Internet or Web is what we’re seeking along the way. VPLS and MPLS are two competing technologies to direct network traffic, letting you have speedy data transfer and communication. What is a VPLS or MPLS network? What’s the difference between VPLS vs MPLS? We’re gonna to elaborate them one by one.
What Is MPLS?
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) is a type of communication that enables a service provider to provision cost effective and flexible “Virtual Private Networks” across a shared core network infrastructure. MPLS is used to send data and network traffic along the most efficient routes, which may be predetermined and are communicated using labels. Packets are carried on predetermined routes along point-to-point connections through label switch routers (LSRs) until they arrive at their destination. In MPLS network, the MPLS switch (eg. FS S5800-48F4S SFP switch) transfers data by popping off its label and sending the packet to the next switch label in the sequence. MPLS perfectly integrates the performance and traffic management capabilities of Layer 2 switching with the scalability and flexibility of Layer 3 routing.
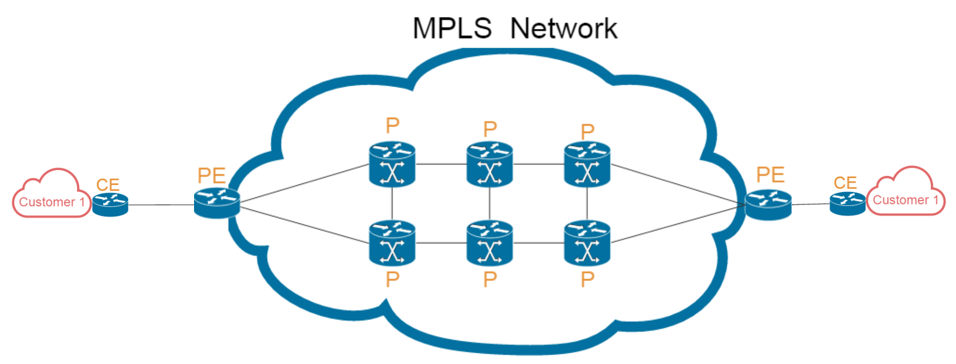
What Is VPLS?
VPLS (Virtual Private LAN Service) is a service that uses MPLS and VPN (Virtual Private Networking) to securely and seamlessly connect multiple LANs over the Internet, making them appear as if they were all on the same LAN. VPLS enables a service provider to extend a Layer 2 network across geographically dispersed sites using a shared core network infrastructure. VPLS works by creating a virtualized Ethernet switch at the provider’s edge to link remote sites. VPLS happens at Layer 2, and the carrier builds out the network, but the customer can do their own routing if they wish. This approach is ideal for corporations that have multiple data center footprints and office or remote locations that require low-latency connections between sites.
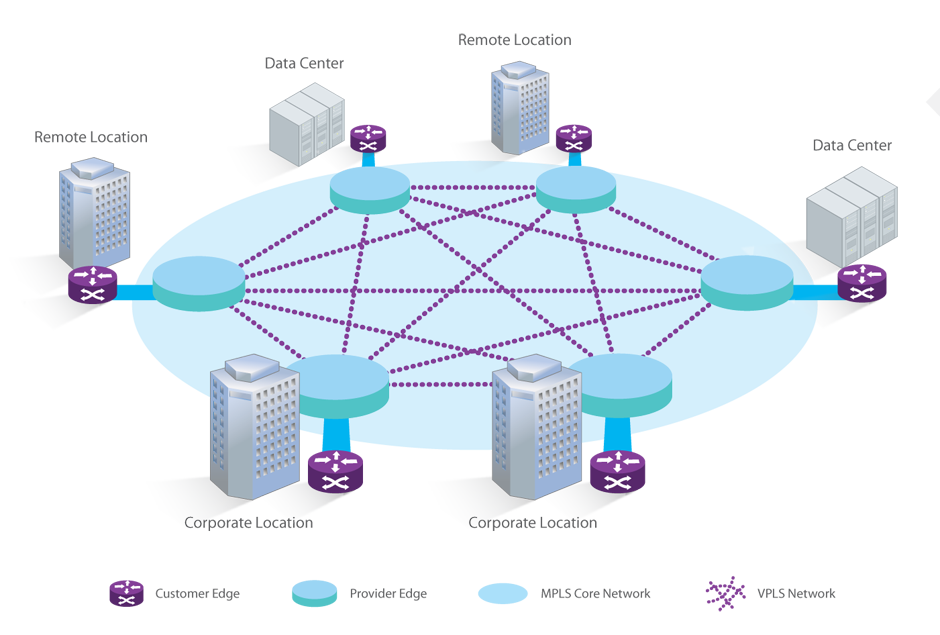
VPLS vs MPLS: Factors to Consider When Choosing Them
When deciding over VPLS vs MPLS for connectivity between remote locations, there are multiple factors to consider. We’ll look into them one by one.
One of the main benefits of VPLS over MPLS are the levels of security offered. As aforementioned, VPLS extend a Layer 2 network across geographically dispersed sites using a shared core network infrastructure. While MPLS perfectly integrates the performance and traffic management capabilities of Layer 2 switching with the scalability and flexibility of Layer 3 routing. VPLS does not share layer 3 routing tables with the service provider, while MPLS may do so, means that VPLS is generally the better solution for highly-sensitive data.
Generally, MPLS can deliver a wider type of network traffic than VPLS. VPLS is typically used for fewer locations that need very high speeds, very simple networks with high performance and high security. Thus, if you desire to connect entities such as data centers across the long-haul network backbone, VPLS is preferable as an Ethernet-based connection strategy. If a customer had hundreds of locations across the country who needs voice, data and video traffic to be carried to all locations, MPLS might make more sense because it is protocol-agnostic and can handle multiple types of traffic. MPLS may be an even clearer choice where large numbers of branches are involved.
Another key difference between MPLS and VPLS is the inherent level of scalability. Due to the manner in which these two technologies interact with your network, MPLS is considered to be far more scalable. Using a backbone of MPLS for maximum network access and scalability, together with VPLS connections for more sensitive data often represents the best possible compromise, you would make the most of both protocols and substantially increase network efficiency.
Conclusion
Although MPLS and VPLS are different technologies, they are not mutually exclusive. Many businesses deploy both MPLS and VPLS protocols within their network in order to get the best of both worlds. FS provides gigabit ethernet switch and 10gbe switch which support both MPLS and VPLS. All these switches comes with rich L2/L3 business processing ability for core switching networks.