Fiber optic communication has developed rapidly in recent years. And in many applications, fiber optic cable has replaced the copper cable for higher speed and higher bandwidth applications. Therefore, numbers of people claim that fiber optic lines have lower latency than copper connections, while others do not think so. Then what’s the latency differences between fiber and copper?
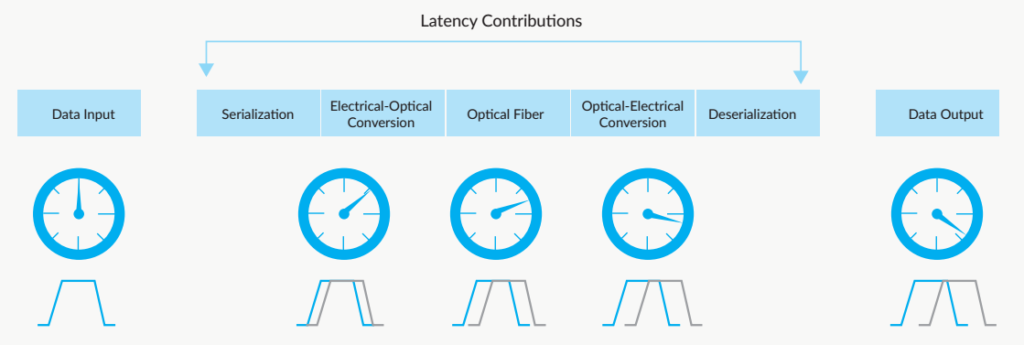
Latency refers to a time delay between stimulation and its response. Usually, it’s caused by velocity limitations in a physical system. Put it in simple terms, latency is the time it takes for a signal to travel from one place to another place. And there are diverse types of latency: network latency, Internet latency, audio latency, WAN latency, etc. No matter in a fiber optic network or a copper network, latency can be described as distance and speed. In addition, latency does exist. It’s just a question of fast or slow. One key factor that affects the latency is the signal speed in transmission media. Fiber and copper are two of transmission media. The type of media used in the communication system depends on the bandwidth and transmission distance required by the application.
As we know, the speed of light in free space is about 3×108 meter per second. While the speed of light in air is slower than that in a vacuum. So does in the glass. Therefore, when an optical signal travels in a fiber link, there are five latency contributors: two are created when the signal moves from the electrical domain to the optical; another contribution occurs as the signal goes through the optical fiber; and as the signal is converted from the optical domain to the electrical, latency occurs.
Signals in copper cables are easy to be interrupted by around environments, especially in long distance transmission. The signals will attenuate as distance increases, which will lead to data transmission error, page error and make users feel slow speed at the moment. Actually, the copper cable transmission speed doesn’t slow down. Besides, alien crosstalk also would cause transmission errors and latency.

Signals are transmitted at 2/3 the speed of light in fiber optic cables. In copper it can be faster than that. However, this cannot account for system latency. In longer distance, latency in the fiber optic system is lower because of less need for processing and repeating of the signals. While signals in copper are affected by electromagnetic interference and are prone to higher rates of loss over long distances.
In addition, no mater in a fiber optic network or a copper network, latency can be described as distance and speed. In addition, during the whole transmission process, serialization delay that shows how fast a data packet can be serialized onto the wire, has far more impact on shorter distances. For example, it will take 8ms to serialize a 1500-byte packet on 1.5Mbps link, while it will only need 1.2us on 10Gbps or less on higher speed. That shows speed makes a significant difference.
In a word, the latency differences between fiber and copper are influenced by transmission distance, speed, and environments. For shorter distance, copper cables can be the first choices, for the delay in it does not mean much and its low cost. For longer distance transmission, fiber cable offers lower latency for the whole network and can be an optimal choice.
Related Articles: What Is Copper Trunk Cable and How to Use It?
Fiber Optic Cable vs Twisted Pair Cable vs Coaxial Cable