Introduction
In the epoch of cloud and intelligence, data center networks play a pivotal role in supporting the seamless integration of cloud services and facilitating robust interconnection between data centers. This article explores the evolving demands, challenges, and innovative solutions in data center networking to meet the requirements of the cloud-centric and intelligent era.
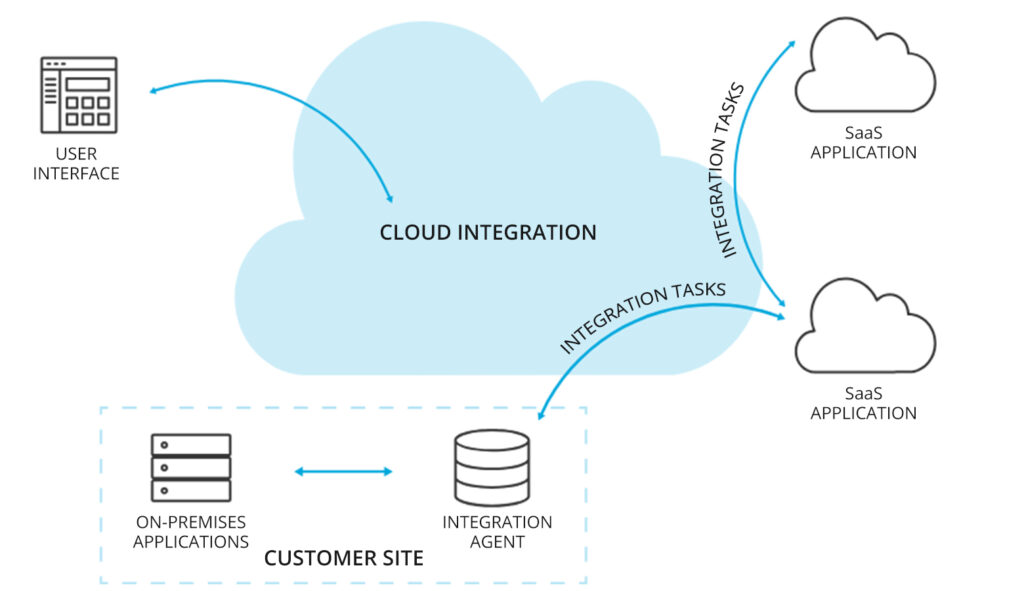
Demand for Cloud Integration
Hybrid Cloud Adoption
Hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines elements of both public and private cloud infrastructures, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both models. In a hybrid cloud setup, certain workloads and data are hosted in a private cloud environment, while others are placed in a public cloud environment. This approach provides flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, enabling organizations to tailor their IT infrastructure to meet specific requirements and optimize resource utilization.
Multi-Cloud Strategy
A multi-cloud strategy is an approach to cloud computing that involves using multiple cloud services from different providers to meet diverse business needs. Rather than relying on a single cloud provider, organizations leverage a combination of public, private, and hybrid clouds to optimize performance, resilience, and flexibility. Organizations leverage multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in, optimize workload placement, and access specialized services, necessitating seamless integration and interoperability between diverse cloud environments.
Edge Computing Expansion
Edge computing expansion refers to the proliferation and adoption of edge computing technologies and architectures to address the growing demand for low-latency, high-performance computing closer to the point of data generation and consumption. As the volume of data generated by IoT devices, sensors, and mobile devices continues to soar, traditional cloud computing models face challenges related to latency, bandwidth constraints, and privacy concerns. Edge computing aims to alleviate these challenges by processing and analyzing data closer to where it is generated, enabling real-time insights, faster decision-making, and improved user experiences.
The proliferation of edge computing drives the need for distributed data processing and storage closer to end-users, requiring integration between centralized data centers and edge computing nodes for efficient data transfer and workload management.
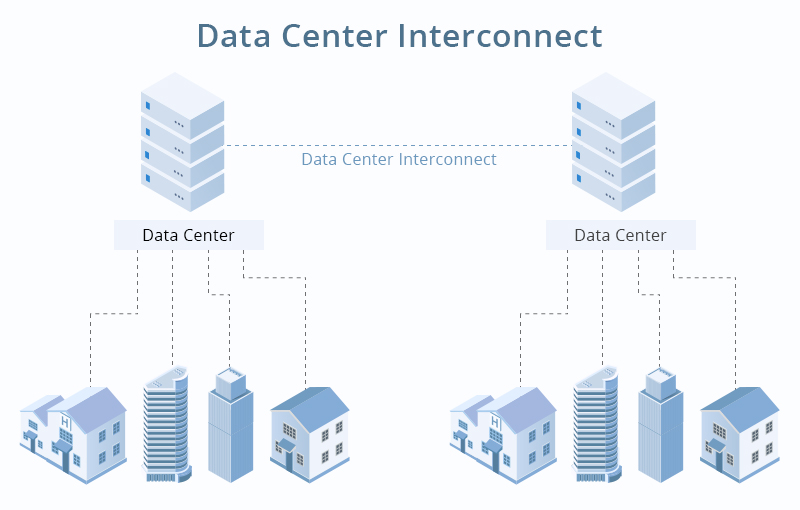
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies in Data Center Interconnection(DCI)
Data center interconnection (DCI) plays a crucial role in enabling seamless communication and data exchange between geographically dispersed data centers. However, several challenges need to be addressed to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and security. Three key challenges in data center interconnection include scalability constraints, network complexity, and security risks.
Scalability Constraints
Scalability constraints refer to the limitations in scaling data center interconnection solutions to accommodate the increasing demand for bandwidth and connectivity. As data volumes continue to grow exponentially, traditional DCI solutions may struggle to keep pace with the requirements of modern applications and workloads.
Challenges
- Limited Bandwidth: Traditional DCI solutions may have limited bandwidth capacities, leading to congestion and performance degradation during peak usage periods.
- Lack of Flexibility: Static or fixed DCI architectures may lack the flexibility to dynamically allocate bandwidth and resources based on changing traffic patterns and application demands.
- High Costs: Scaling traditional DCI solutions often requires significant investments in additional hardware, infrastructure upgrades, and network bandwidth, leading to high operational costs.
Mitigation Strategies
- Scalable Architecture: Adopting scalable DCI architectures, such as optical transport networks (OTNs) and software-defined networking (SDN), enables organizations to dynamically scale bandwidth and capacity as needed.
- Cloud Bursting: Leveraging cloud bursting capabilities allows organizations to offload excess workloads to cloud providers during peak demand periods, reducing strain on internal data center interconnection resources.
- Network Virtualization: Implementing network virtualization techniques enables the abstraction of physical network resources, allowing for more efficient resource utilization and scalability.
Network Complexity
Network complexity refers to the challenges associated with managing and maintaining interconnected data center networks, particularly in heterogeneous environments with diverse technologies, protocols, and architectures.
Challenges
- Interoperability Issues: Integrating data centers with different networking technologies and protocols may result in interoperability challenges, hindering seamless communication and data exchange.
- Configuration Management: Managing configurations, policies, and routing protocols across interconnected data center networks can be complex and error-prone, leading to configuration drifts and network instability.
- Traffic Engineering: Optimizing traffic flows and routing paths across interconnected data centers requires sophisticated traffic engineering techniques to minimize latency, congestion, and packet loss.
Mitigation Strategies
- Standardization: Adopting industry-standard networking protocols and technologies facilitates interoperability and simplifies integration between heterogeneous data center environments.
- Automation: Implementing network automation tools and orchestration platforms automates configuration management, provisioning, and monitoring tasks, reducing manual errors and improving operational efficiency.
- Centralized Management: Centralizing management and control of interconnected data center networks through centralized management platforms or SDN controllers enables consistent policy enforcement and simplified network operations.
Security Risks
Security risks in data center interconnection encompass threats to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data transmitted between interconnected data centers. With data traversing public networks and spanning multiple environments, ensuring robust security measures is paramount.
Challenges
- Data Breaches: Interconnected data center networks increase the attack surface and exposure to potential data breaches, unauthorized access, and cyber attacks, especially when data traverses public networks.
- Compliance Concerns: Maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and data protection laws across interconnected data center networks poses challenges in data governance, privacy, and risk management.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring the integrity of data transmitted between interconnected data centers requires mechanisms for data validation, encryption, and secure transmission protocols to prevent data tampering or manipulation.
Mitigation Strategies
- Encryption: Implementing end-to-end encryption and cryptographic protocols secures data transmission between interconnected data centers, safeguarding against eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Enforcing strict access control policies and authentication mechanisms restricts access to sensitive data and resources within interconnected data center networks, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and insider threats.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Implementing comprehensive auditing and monitoring solutions enables organizations to detect and respond to security incidents, anomalies, and unauthorized activities in real-time, enhancing threat detection and incident response capabilities.
By addressing scalability constraints, network complexity, and security risks in data center interconnection, organizations can build resilient, agile, and secure interconnected data center networks capable of meeting the demands of modern digital business environments.
Benefits of Cloud-Integrated Data Center Networking
Cloud-integrated data center networking brings together the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing with the control and security of on-premises data centers. This integration offers numerous benefits for organizations looking to modernize their IT infrastructure and optimize their operations. Three key aspects where cloud-integrated data center networking provides significant advantages include improved agility, enhanced performance, and enhanced security.
Improved Agility
Cloud-integrated data center networking enhances agility by enabling rapid provisioning, scaling, and management of IT resources to meet changing business demands.
- Resource Flexibility: Organizations can dynamically allocate compute, storage, and network resources based on workload requirements, optimizing resource utilization and reducing infrastructure sprawl.
- Automated Provisioning: Integration with cloud services enables automated provisioning and orchestration of IT resources, streamlining deployment workflows and accelerating time-to-market for new applications and services.
- Scalability: Cloud-integrated networking allows organizations to scale resources up or down quickly in response to fluctuating demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency without over-provisioning or underutilization.
Enhanced Performance
Cloud-integrated data center networking enhances performance by leveraging cloud services and technologies to optimize network connectivity, reduce latency, and improve application responsiveness.
- Global Reach: Integration with cloud providers’ global networks enables organizations to extend their reach to diverse geographic regions, ensuring low-latency access to applications and services for users worldwide.
- Content Delivery: Leveraging cloud-based content delivery networks (CDNs) improves content delivery performance by caching and distributing content closer to end-users, reducing latency and bandwidth consumption for multimedia and web applications.
- Optimized Traffic Routing: Cloud-integrated networking platforms use intelligent traffic routing algorithms to dynamically select the best path for data transmission, minimizing congestion, packet loss, and latency across distributed environments.
Enhanced Security
Cloud-integrated data center networking enhances security by implementing robust encryption, access control, and threat detection mechanisms to protect data and applications across hybrid cloud environments.
- Data Encryption: Integration with cloud services enables organizations to encrypt data both in transit and at rest, ensuring confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information, even when traversing public networks.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Cloud-integrated networking platforms support centralized IAM solutions for enforcing granular access control policies, authentication mechanisms, and role-based permissions, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and insider threats.
- Threat Detection and Response: Integration with cloud-based security services and threat intelligence platforms enhances visibility and detection of security threats, enabling proactive threat mitigation, incident response, and compliance enforcement across hybrid cloud environments.
FS N5850-48S6Q cloud data center switch supports the installation of compatible network operating system software, including the commercial product PicOS. Equipped with dual power supplies and smart fans by default, providing high availability and long life. Deploy modern workloads and applications with optimized data center top-of-rack (ToR) networking solutions. Sign up and buy now!
By leveraging cloud-integrated data center networking, organizations can achieve greater agility, performance, and security in managing their IT infrastructure and delivering services to users and customers. This integration allows businesses to capitalize on the scalability and innovation of cloud computing while maintaining control over their data and applications in on-premises environments, enabling them to adapt and thrive in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
Final Words
In conclusion, the future of cloud-integrated data center networking holds immense promise for organizations seeking to harness the full potential of cloud computing while maintaining control over their data and applications. By embracing emerging technologies, forging strategic partnerships, and adopting a forward-thinking approach to network architecture, organizations can build agile, secure, and resilient hybrid cloud environments capable of driving innovation and delivering value in the digital era. As businesses continue to evolve and adapt to changing market dynamics, cloud-integrated data center networking will remain a cornerstone of digital transformation strategies, enabling organizations to thrive in an increasingly interconnected and data-driven world.
FS can provide a wide range of solutions with a focus on customer satisfaction, quality and cost management. Our global footprint dedicated and skilled professionals, and local inventory will ensure you get what you need, when you need it, no matter where you are in the world. Sign up now and take action.